What is Honeymoon Cystitis in Males
Honeymoon cystitis is a type of urinary tract infection (UTI) that commonly affects males, particularly after periods of increased sexual activity. It’s characterized by inflammation of the bladder, leading to a range of uncomfortable symptoms. The condition is often temporary and treatable, but understanding its causes, symptoms, and prevention methods is crucial for effective management. This article provides a comprehensive guide to honeymoon cystitis in males, detailing everything from the initial causes to the best ways to prevent and treat it.
Understanding the Term
The term ‘cystitis’ refers to the inflammation of the bladder. When this inflammation is associated with sexual activity, it’s often dubbed ‘honeymoon cystitis.’ The name stems from the fact that the condition is frequently observed during honeymoons or periods when couples engage in more frequent sexual intercourse. This increased activity can introduce bacteria into the urethra, potentially leading to an infection. It’s essential to recognize that while the name suggests a romantic context, the underlying issue is a medical one that needs attention and care.
Why it’s Called Honeymoon Cystitis

The moniker ‘honeymoon cystitis’ is primarily related to the timing and context in which the condition often arises. During honeymoons or periods of increased sexual activity, the frequency and nature of sexual encounters can elevate the risk of developing a UTI. The mechanical actions of intercourse can irritate the urethra and potentially push bacteria into the bladder. Moreover, the increased likelihood of bacteria transfer during sex, combined with reduced personal hygiene habits, can contribute to the onset of the infection, hence the term, which highlights this connection between sexual activity and the development of cystitis.
Symptoms of Honeymoon Cystitis in Males
Recognizing the symptoms of honeymoon cystitis is the first step towards seeking treatment. These symptoms can vary in intensity but generally include discomfort and changes in urinary habits. Early detection helps in effective management and can prevent the infection from escalating. Understanding the range of symptoms and their implications can assist in prompt and appropriate medical attention. The following sections will delve deeper into the specific symptoms to watch out for, helping in quicker and accurate self-assessment.
Common Symptoms to Watch For
The most common symptoms include a frequent urge to urinate, even when the bladder is not full. This can be accompanied by a burning sensation during urination, known as dysuria. Many individuals also report a feeling of pressure or pain in the lower abdomen or the bladder area. The urine may appear cloudy, and sometimes, there may be blood present, indicating a more severe infection. Other symptoms to watch for include a low-grade fever and general malaise. The appearance of any of these symptoms requires prompt attention.
Severity and Duration

The severity of honeymoon cystitis can vary, ranging from mild discomfort to intense pain. For some, the symptoms are transient, resolving within a few days with home remedies. However, in other cases, the infection can become more severe, leading to significant discomfort and potentially spreading to the kidneys if left untreated. The duration also varies, with some cases resolving quickly, while others may persist for a week or more. The infection can recur if the underlying causes are not addressed. Seeking medical advice and treatment is essential, especially if symptoms worsen or fail to improve after a few days.
Top 5 Facts About Honeymoon Cystitis in Males
Understanding the key facts about honeymoon cystitis can empower males to take proactive steps towards prevention and effective management. The following facts shed light on the most critical aspects of this condition, from its primary causes to the available treatment options. Grasping these essential points can provide clarity and guidance in dealing with and preventing honeymoon cystitis. These points are vital to understanding the root causes and effective ways to manage the infection.
Fact 1 Increased Sexual Activity
Increased sexual activity is a primary trigger for honeymoon cystitis. More frequent intercourse can cause friction and irritation in the urethra, which can facilitate the entry of bacteria. This increased activity may also mean more opportunities for bacteria to be introduced into the urinary tract. Therefore, understanding the relationship between sexual activity and cystitis is crucial for implementing preventive measures. Adjusting hygiene practices and monitoring bodily responses can significantly help in reducing the risks associated with heightened sexual encounters. This is particularly important for individuals starting new relationships or during periods of increased sexual frequency.
Fact 2 Bacterial Infection

Honeymoon cystitis is primarily caused by bacterial infections, most commonly involving bacteria that enter the urethra and ascend to the bladder. These bacteria may originate from the skin, the genital area, or through sexual contact. The bacterium, Escherichia coli (E. coli), is a frequent culprit, often found in the digestive tract. Preventing the introduction of bacteria requires meticulous hygiene practices before and after sexual activities. If bacteria manage to colonize the bladder, they can quickly multiply, causing the inflammation and other symptoms characteristic of a UTI.
Fact 3 Urinary Tract Irritation
The mechanical aspects of sexual intercourse can irritate the urinary tract. This irritation can make it easier for bacteria to attach to the bladder walls. Furthermore, the urethra’s proximity to the anus means that bacteria can easily migrate from the perianal area into the urinary tract. Irritation can also be caused by spermicides, lubricants, and other products used during sexual activity. Choosing gentle and non-irritating products can mitigate the risk. Proper hygiene can effectively minimize the risk of bacterial infection and consequent irritation. Hydration is crucial for flushing out potential bacteria.
Fact 4 Importance of Hydration
Adequate hydration is vital in the prevention and treatment of honeymoon cystitis. Drinking plenty of water helps to flush bacteria out of the urinary tract, reducing the likelihood of infection. Regular urination, facilitated by increased fluid intake, prevents bacteria from adhering to the bladder walls. Water dilutes the urine, decreasing the concentration of bacteria and irritants. During and after sexual activity, it’s especially important to increase fluid intake to help maintain urinary health. Monitoring hydration levels can thus play a key role in preventing recurrent UTIs.
Fact 5 Prophylactic Antibiotics

In some cases, doctors may prescribe prophylactic antibiotics to prevent recurrent honeymoon cystitis. These antibiotics are taken before or immediately after sexual activity to prevent bacterial infections from establishing themselves in the urinary tract. This approach is particularly considered for individuals with frequent or severe UTIs. It is important to remember that while effective, prophylactic antibiotics are used cautiously due to the risk of antibiotic resistance. Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial to determining the right course of action and whether this is the appropriate option for managing UTIs.
Preventing Honeymoon Cystitis in Males
Preventing honeymoon cystitis involves a combination of good hygiene practices, lifestyle adjustments, and informed sexual health habits. Being proactive in these areas can significantly reduce the risk of developing UTIs. The following sections outline key preventive measures that can be adopted to maintain urinary tract health and reduce the chances of experiencing symptoms. Integrating these preventive measures can greatly improve the quality of life and sexual experiences, by minimizing the risks associated with this condition.
Pre-Sex Hygiene
Practicing good hygiene before sexual activity can significantly reduce the risk of bacterial entry into the urethra. This includes washing the genital area with mild soap and water. Both partners should clean their genital areas to remove any potential bacteria that might be present. The use of clean hands and clean sex toys also helps in preventing bacteria from entering the urinary tract. Avoiding the use of harsh soaps and fragrances, as these can irritate the skin and increase susceptibility to infection. Prioritizing pre-sex hygiene is a simple, yet effective measure in preventing honeymoon cystitis.
Post-Sex Hygiene
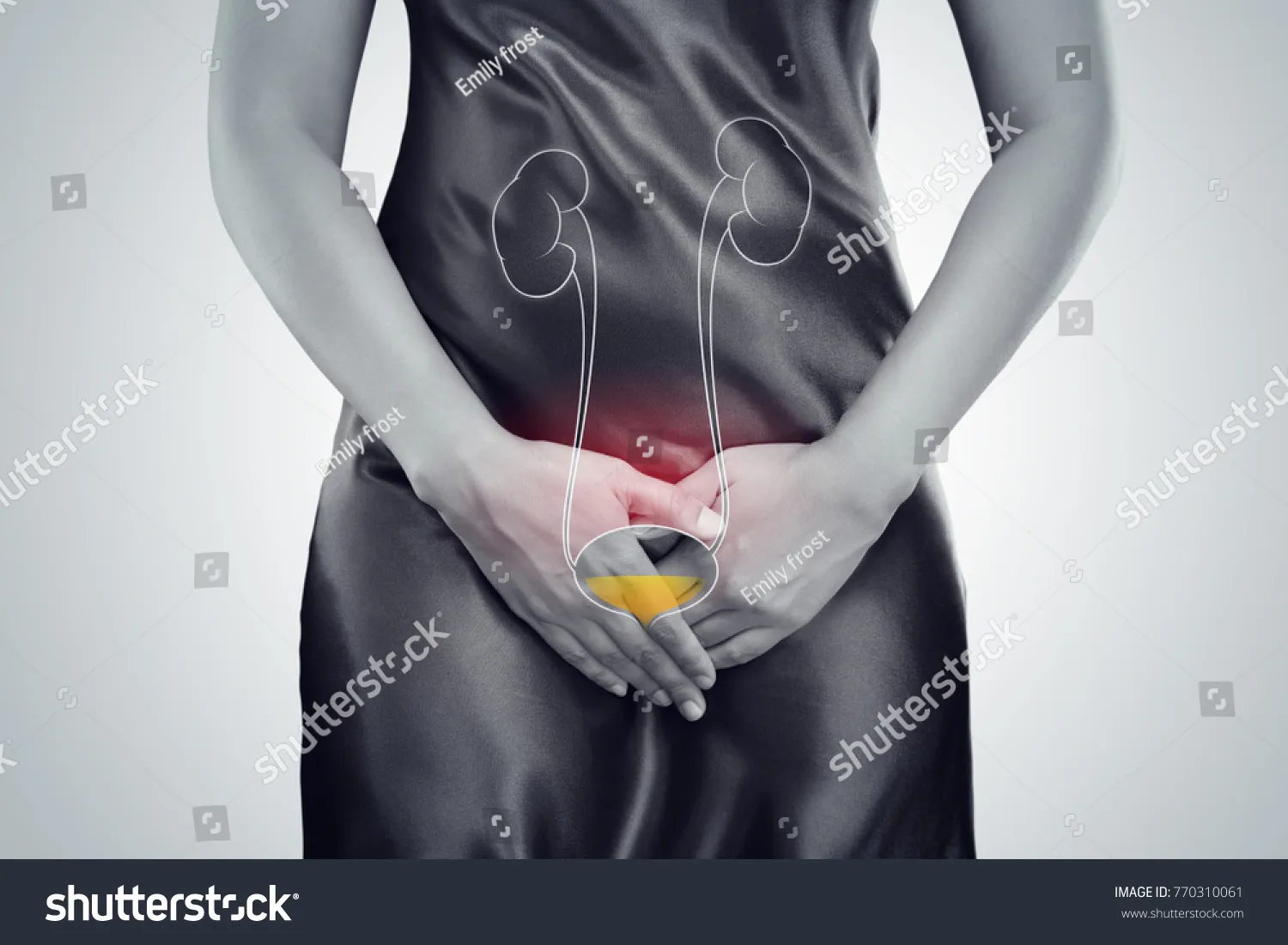
Post-sex hygiene is just as important as pre-sex practices. Urinating after intercourse helps flush out any bacteria that may have entered the urethra during sexual activity. Washing the genital area gently with water can also help to remove bacteria. For males, this may involve retracting the foreskin (if uncircumcised) and washing the area thoroughly. Encouraging both partners to urinate and clean themselves after sex ensures that any potential bacteria are removed, which helps in preventing the onset of a UTI. Making these hygiene routines consistent can significantly lower the risk.
Hydration and Frequent Urination
Maintaining adequate hydration and urinating frequently is crucial for preventing UTIs. Drinking plenty of water helps dilute the urine, making it less favorable for bacterial growth. Frequent urination helps to flush out bacteria from the bladder before they can multiply and cause an infection. Aim to drink several glasses of water daily and urinate whenever the urge arises, especially after sexual activity. This simple practice is one of the most effective measures in preventing honeymoon cystitis and promoting urinary tract health. Making hydration a priority can significantly reduce the chances of experiencing a UTI.
Treating Honeymoon Cystitis in Males
Treating honeymoon cystitis typically involves medical interventions and home remedies aimed at alleviating symptoms and eradicating the infection. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent the infection from spreading to the kidneys. The following sections will explore the various options available for effectively managing and treating this condition. Effective treatment strategies may combine medical options and self-care methods, aimed at ensuring comfort and recovery.
Medical Treatment Options
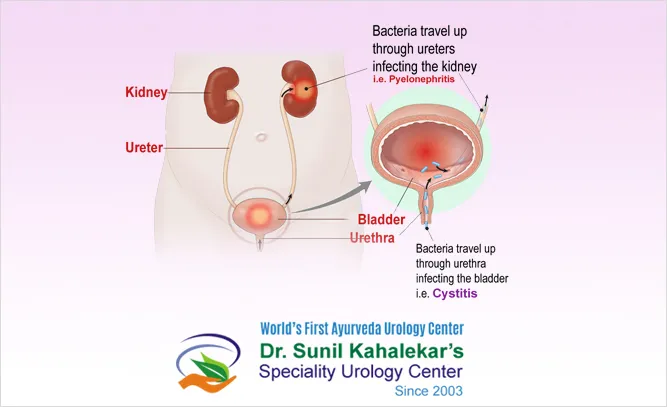
Medical treatment for honeymoon cystitis generally involves antibiotics, prescribed by a healthcare provider, to kill the bacteria causing the infection. The choice of antibiotic depends on the specific bacteria and the individual’s medical history. In some cases, doctors may prescribe pain relievers to alleviate discomfort. It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve. Following the doctor’s instructions carefully ensures effective treatment and minimizes the risk of recurrent infections. If symptoms do not improve within a few days, a follow-up appointment might be necessary for further evaluation.
When to See a Doctor
It is important to see a doctor if you experience symptoms of honeymoon cystitis, especially if they are severe or persist. Seek medical attention if you notice blood in your urine, have a fever, or experience flank pain (pain in the side or back), which could indicate a kidney infection. Prompt medical evaluation ensures accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Early intervention can prevent complications. If symptoms do not improve after a few days of treatment or if they recur frequently, consult your doctor to explore potential underlying causes and more effective management strategies. A medical professional can offer appropriate guidance tailored to individual needs and conditions.
Living with Honeymoon Cystitis
Living with honeymoon cystitis involves understanding and managing the condition to minimize its impact on daily life. This includes knowing how to recognize the symptoms, take preventive measures, and seek timely treatment. With the right strategies, individuals can lead healthy and fulfilling lives, even if prone to UTIs. Proactive steps and awareness are crucial for handling this health concern effectively. Learning how to deal with the condition can empower individuals to control their health and well-being.
